Are the Skills in Your Hands Built for Athletes?
PACE-Approved Online Course for Chiropractors & Physiotherapists
Bridge the Gap Between Theory and Clinical Excellence
Develop sharper assessment skills, build confidence in your clinical reasoning, and earn CME credits — all while learning from one of the world’s premier clinicians.
Don't Trust Us, Trust Our Results...
Learn the exact methods used by top clinicians.
Dr. Michael Prebeg has spent over two decades working with professional athletes in the NHL, MLB, and beyond. In this course, he teaches the exact assessment and treatment frameworks he uses to achieve consistent, measurable results with the world’s best
Identify dysfunctional movement patterns using the Adaptive Potential Model
Build outcome-driven treatment plans that create lasting results
Confidently assess and treat complex neuromechanical cases
Earn 12 CME hours while advancing your real-world clinical skillset
We Want You To Master The Basics
The FIFA method teaches you a structured process for neurofunctional evaluation and treatment.
FIFA Doesn’t Replace Your Skills... It Improves Them by building up the foundation

THE FIFA ROADMAP
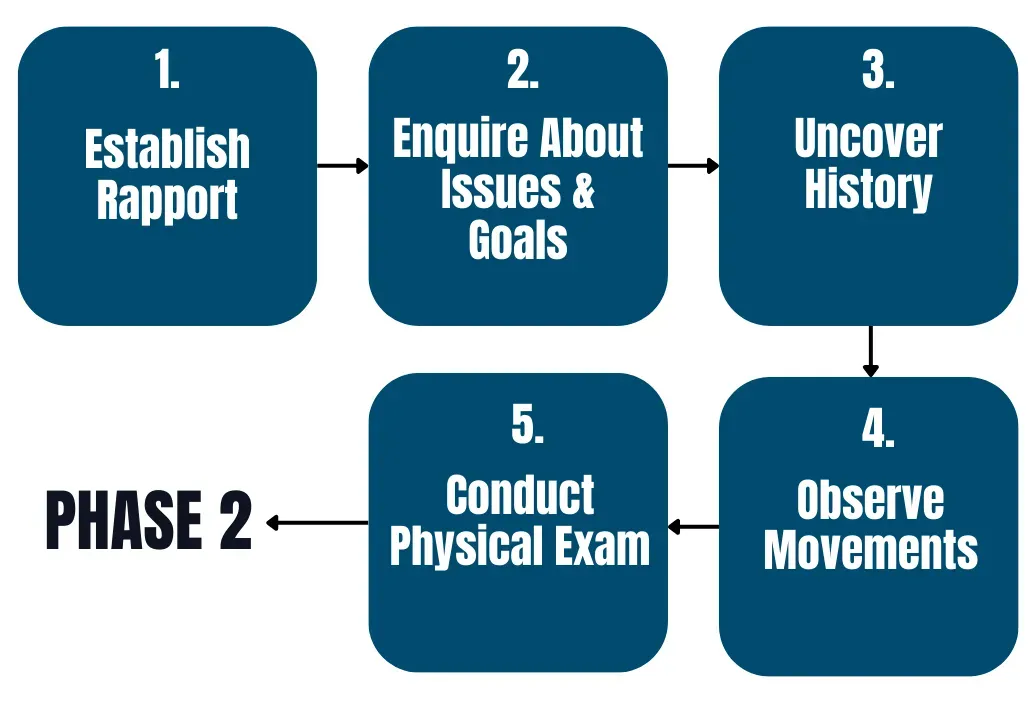
Phase 1
Turns history + movement into a predictive clinical map
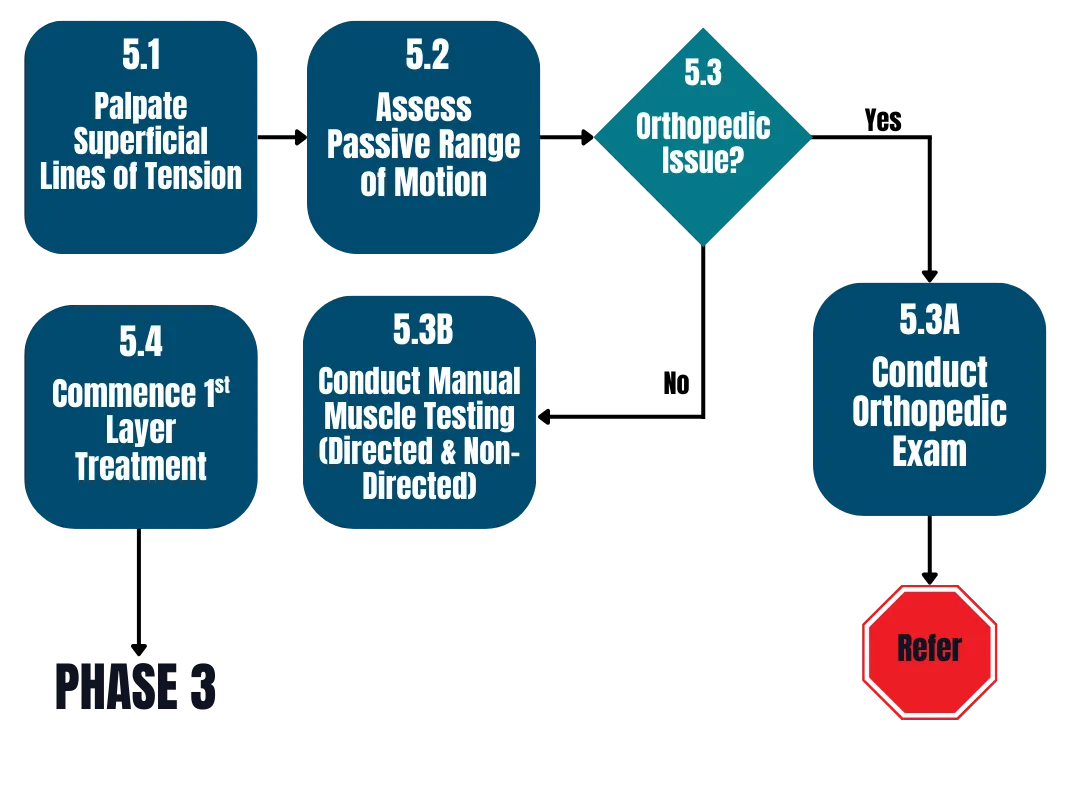
Phase 2
Stress-tests the map; exposes hidden drivers beyond structure
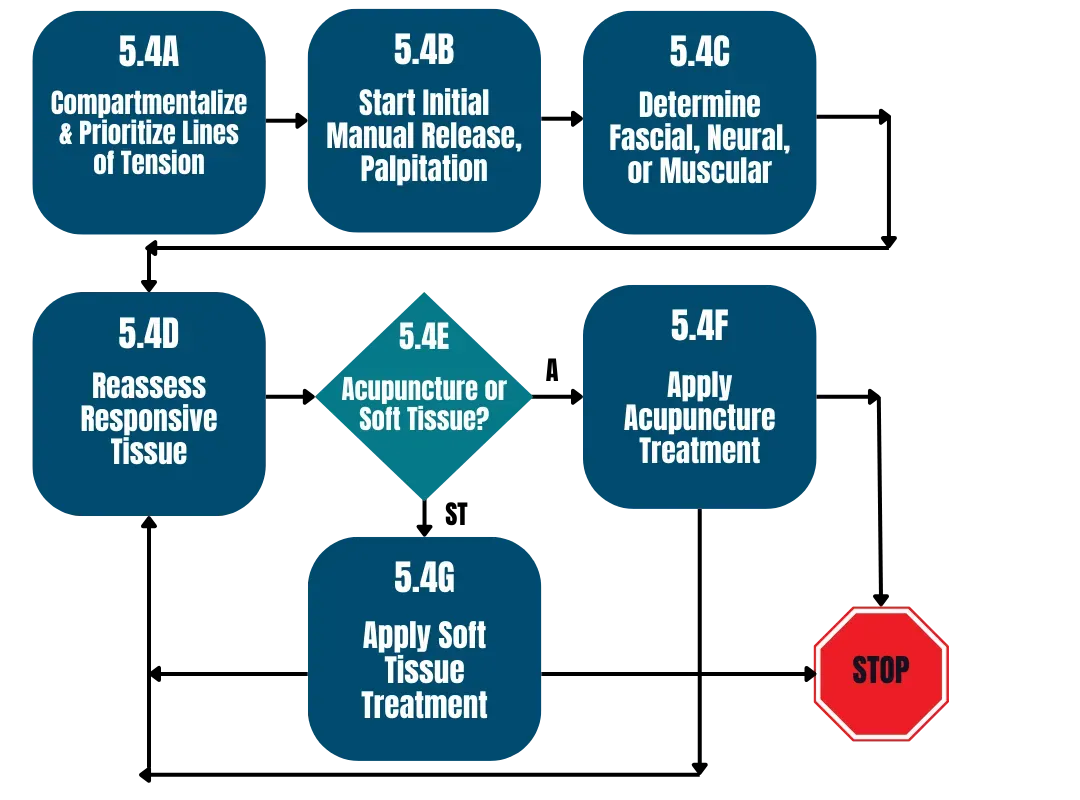
Phase 3
Decodes fascial / muscular / neural roots and locks in change
What you get with fIFA
3 Core Classes (recorded live)
Step-by-step walk-through of the full FIFA system, shot at the in-person event so you see every nuance.
3 Guest-Expert Assessments
Ortho surgery with Dr. John Theodoropoulos, Matt Nichol/ Advanced neuromotor testing with Dr. Alejandro Elorriaga
Full Neuromuscular Evaluation
Watch the full upper- and lower-body treatment process to optimize performance in elite professional athletes.
3 Live Virtual Coaching Calls
Small-group live assessment demonstration and Q&A with Mike after each module
1-Year On-Demand Access
Re-watch, pause, and review the modules as many times as you need.
Cheat-Sheets
& Flow Maps
Phase checklists, nerve charts, and the Algorithm diagram for your clinic.
Listen to what the graduates have to say
"The beauty of the course is in the simplicity. The model helps clearly compartmentalize issues of Neuro - MSK complaints and helps piece the global dysfunction for treating."
"Now that I have taken the FIFA course, I feel extremely confident to begin clinical practice because I have a systematic approach to assess dysfunction."
"FIFA is the fastest way to become one of them."

What Does It Cost?
This Program Will Eventually Cost Over $3,000… But Not For You
We are offering a special offer, for $1,700 USD up front you can get everything for your clinic!
If our offer of $1,700 is too much up front, don't worry we are also offering a 3 month plan where you can get all of the benefits of FIFA for 3 easy payments of $620 USD per month!
But if you aren't satisfied, you can get...

100% Money-Back Guarantee. No Questions Asked.
If You're Not Blown Away, You Get Your Money Back!
If you don’t see clearer assessments, better clinical direction, and patients who stick with the plan...
email us and we will return every dollar
No hoops. No small print.
Because when you apply FIFA, you should earn back your investment well inside 90 days—often sooner.
That’s our promise, and we’ll stand behind it.
Is FIFA For You?
To enroll, you must have:
An active healthcare license issued by a state or national credentialing board
OR
Be enrolled in a healthcare degree program at an accredited post-secondary institution, that requires a license from a state or national credentialing board to practice in your field of study post-graduation.
A Certificate of Completion is provided for those seeking continuing education credits:
1) 6 CE credits for foundations in functional assessment online
2) PACE approved for CE credits in US
3) Recognized by the PACE program of Federation of Chiropractic Licensing Boards
All healthcare professionals listed below can benefit from taking FIFA.
Manual therapists that treat musculoskeletal conditions will benefit the most.
Acupuncturists
Chiropractors
Massage Therapists
Medical Doctors
Naturopaths
Occupational Therapists
Osteopaths
Physiotherapists
Registered Kinesiologists
DON'T MISS THE CHANCE TO WORK WITH DR. MIKE PREBEG
©2025 Skills-In-Hand